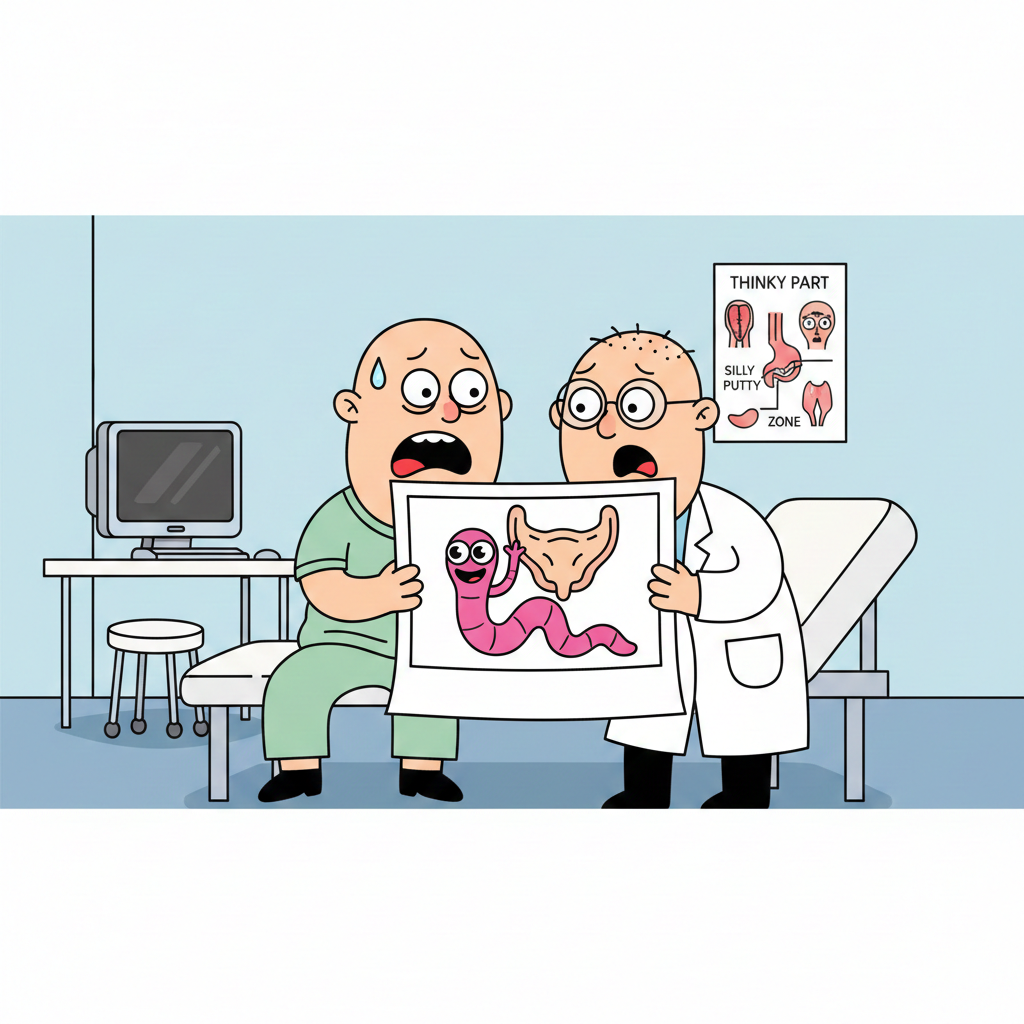
A disturbing video captures the moment when an ultrasound examination uncovered minuscule worms wriggling inside a man’s scrotum. The 26-year-old individual, hailing from New Delhi, India, sought help at a sexual health clinic due to discomfort and swelling in his right testicle.
To the astonishment of doctors, the ultrasound revealed the presence of “linear structures in motion” within a narrow tube responsible for transporting fluid and white blood cells in the scrotum. The patient, who remained unnamed, received a diagnosis of lymphatic filariasis and was prescribed a three-week course of an anti-parasitic medication. Upon his return, the worms had vanished.
This unsettling case follows a previous incident in which a Venezuelan man sought medical attention after claiming that thieves inserted a beer bottle into his rectum.
Dr. Amit Sahu, a senior medical consultant at Max Super Speciality Hospital who examined the patient, noted that the ultrasound displayed “the undulating movements of live worms.” These worms had migrated into the lymphatic system, leading to dilation and dysfunction of the channels.
Further examination involved the extraction of fluid from the scrotum, which, when examined under a microscope, also revealed a multitude of live worms scientifically known as Wuchereria bancrofti, thus confirming the diagnosis. The patient was subsequently treated with diethylcarbamazine, a potent anti-parasitic drug effective against the worms.
Upon returning for a follow-up three weeks later, another ultrasound confirmed the absence of the worms, and the patient experienced a full recovery.
Lymphatic filariasis infections are typically transmitted through mosquito bites, as these insects transfer the parasites into the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, the worms travel into the lymphatic system, a network designed to drain fluid, eventually reaching various parts of the body, including the scrotum.
Within the lymphatic system, these parasites mature, reproduce, and release millions of offspring. Usually, these worms do not trigger any noticeable symptoms. However, in certain cases, damage to the lymphatic system leads to fluid accumulation in the legs, resulting in lymphedema. In more severe instances, characterized by substantial limb swelling, individuals are diagnosed with elephantiasis. In men, the presence of these parasitic worms can lead to genital swelling, which, in extreme cases, causes disfigurement and mobility problems.
The primary treatment for this disease involves antiparasitic medications. Lymphatic filariasis infections are relatively common in tropical and subtropical regions, including parts of Africa, Asia, and South America. These infections are not present in the United States or the United Kingdom.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasize that individuals need to be repeatedly bitten by infected mosquitoes over several months to contract the infection. Short-term tourists have a very low risk of infection. However, people residing in tropical or subtropical areas where the disease is prevalent face the greatest risk.
The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies lymphatic filariasis as a neglected tropical disease. Estimates suggest that over 50 million people worldwide are infected with this disease. Nevertheless, the WHO asserts that the disease could be eradicated if annual doses of anti-parasitic drugs were distributed to at-risk regions.